a theropod in the family Tyrannosauridae. Fossils from the late Cretaceous Period have been found in Alberta.
Mesozoic Timeline
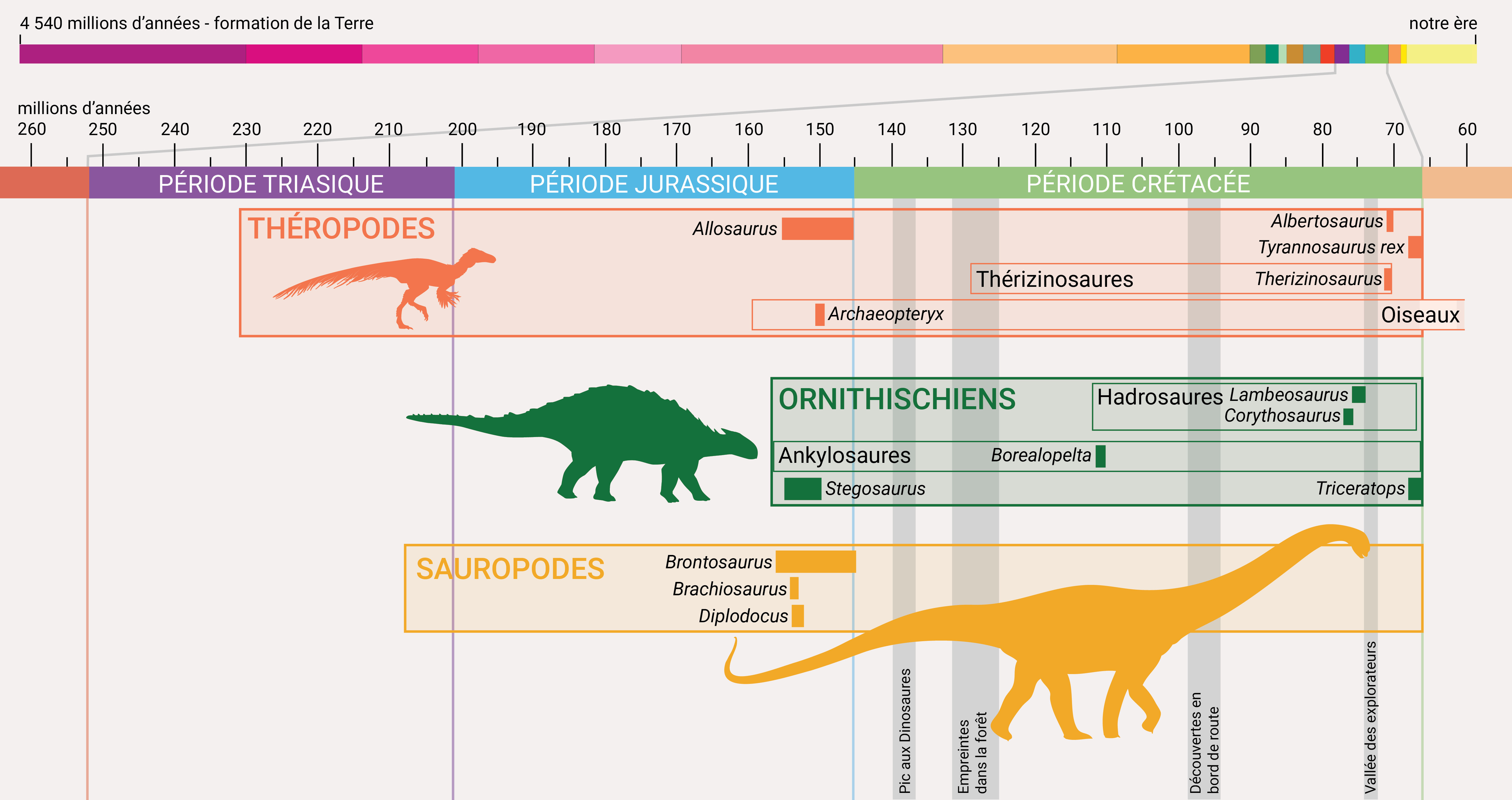



a theropod in the family Tyrannosauridae. Fossils from the late Cretaceous Period have been found in Alberta.
a large theropod dinosaur from the late Jurassic Period. Fossils have been found in the western United States.
Armoured dinosaurs that walked on four feet and ate plants. Different types of ankylosaurs have been found from the late Jurassic to the end of the Cretaceous.
an upward bend in a geologic layer, forming an arch-like shape.
one of the early fossil dinosaurs found with feathers. The first specimen, found in Germany, helped to establish dinosaurs as the ancestors of modern birds.
warm-blooded vertebrate animals with feathers, descended from theropod dinosaurs.
when all or part of the organism itself, like a bone, becomes a fossil.
a nodosaur-type ankylosaur from the Cretaceous Period. A very well-preserved fossil was found in Alberta in 2011.
a large sauropod from the late Jurassic Period with longer front legs than back legs. Fossils have been found in the western United States.
a large sauropod up to 22 metres long from the late Jurassic Period. Fossils have been found in the western United States.
a crested hadrosaur known from the late Cretaceous Period in North America.
shaped like a crescent, or half-moon.
A span of time from 145 to 66 million years ago. The dinosaurs went extinct at the end of the Cretaceous Period, except for the ancestors of modern birds.
When sediment is moved by water, wind, or ice and collects somewhere new.
a large sauropod (up to 26m long) from the late Jurassic Period with a very long tail. Fossils have been found in mid-western North America.
Large stones that dropped into sediments before they became rock. They are often dropped from melting ice floating over bodies of water.
A crack between two faces of rock.
Flat lands near rivers that collect extra water when the rivers flood.
Layers of rock that have been curved or bent.
Small hills at the base of mountains that slowly increase in elevation.
an organism, or a trace of an organism, that has become preserved as stone in the Earth’s crust.
The sediment left behind by moving glaciers.
Global Positioning System, which uses satellites to pinpoint a location on Earth using latitude and longitude.
When grains of sediment are sorted from the top to bottom of a rock bed based on size.
an animal that only eats plants.
A material made of decaying plant and animal matter.
a Latin phrase meaning “in its original place”. If fossils are left in situ, we can learn more about them from the surrounding environment.
a span of time from 201 to 145 million years ago. The first birds are known from the Jurassic Period.
a crested hadrosaur that lived about 75 million years ago. The University of British Columbia has a full Lambeosaurus skeleton on display in the Pacific Museum of Earth.
A soft, brown sedimentary rock made from compressed organic matter.
The process of soft sediment being turned into rock.
Lisa and Richard’s name for the types of dinosaurs that made lumpy footprints that are difficult to identify.
The largest and steepest peaks in a mountain range.
the shape of an organism, or the shape of part of an organism.
a type of ankylosaur that didn’t have a club at the end of its tail.
an animal that eats both meat and plants.
a group of plant-eating dinosaurs whose name means “bird-hipped”.
Rock beds that face a different direction from when they were formed.
a scientist who studies ancient life through fossils.
The geological material that soil forms from.
Partially decayed plant matter.
when one animal eats another animal for food.
the largest of the dinosaurs, sauropods had long necks with small heads, long tails, and walked on four strong legs.
A layer of soil that has different characteristics than the layers next to it.
a plant-eating dinosaur with upright plates along its back, from the late Jurassic Period
a downward bend in a geologic layer, forming a U-shape.
an unusual plant-eating theropod with very long claws and four-toed footprints.
mostly meat-eating dinosaurs that walked on two legs. Theropods are the group that gave rise to modern birds.
when a mark made by an organism, such as a footprint, becomes a fossil.
a span of time from 252 to 201 million years ago. The first dinosaurs are from the Triassic Period.
a plant-eating dinosaur with three horns on its head, found in the late Cretaceous Period.
a rounded projection of the skin, such as those seen in detailed skin impressions of dinosaur feet.
a family of many different large meat-eating theropod dinosaurs from the Cretaceous Period.
a very large (up to 12-metre long) theropod that lived in what is now North America at the end of the Cretaceous Period.
When touching rock beds were formed at very different times. This creates a gap in the geological record of a landscape.
a four-footed mammal, usually with hooves, like a deer.